Orthopedic Designs North America, Inc. - SLN Nail & Distal Fix
The Talon™ DistalFix™ Proximal Femoral Nail’s primary indications are for fixation/stabilization of stable and unstable fractures of the proximal femur including:
Indications
The Talon™ DistalFix™ Proximal Femoral Nail’s primary indications are for fixation/stabilization of stable and unstable fractures of the proximal femur including:
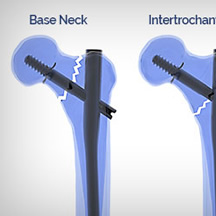
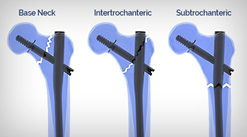
- Intertrochanteric fractures,
- Pertrochanteric fractures,
- High subtrochanteric fractures (without shaft extension)
- Combinations of these fractures.
- The long nail allows the additional indication of low subtrochanteric fractures.
The device is intended to stabilize fragments of the fracture until bony union can occur.
Contraindications
- Active local infection
- Metal sensitivity or allergic reaction to foreign bodies
- Loss of bone stock or insufficient bone quality to support the device
- Obliterated medullary canal
- Comminuted fractures
- Fractures of the distal third
- Femoral neck fractures
Orthopedic Designs North America - Distal Fix
The Talon™ DistalFix™ Proximal Femoral Nail was evaluated using a series of biomechanical tests to establish the following:
- Talon™ superiority over our existing stainless steel cortical screw;
- Axial fatigue strength of the distal Talons™;
- Rotational stability of the distal Talons™;
- Overall performance as the total construct
Distal Talon™ Superiority
Establishing distal Talon™ superiority over our existing stainless steel cortical screw was vital for proof of concept. To do this, the proximal ends of two composite femora were removed and the stainless and DistalFix™ nails were implanted such that the distal tips of the nails were approximately 48mm superior of the distal femur. A static load was applied to the tops of the nails under displacement control. The results showed the Talon™ DistalFix™ nail requires more force for a given displacement.
Axial Fatigue Strength
The durability of the distal Talons™ was determined by applying a cyclic load to the proximal nail in a manner similar to the static pushout test shown previously. The cyclic load was established at 98N to 980N based on a past study of a similar construct and displacement of the nail was recorded. The results of two tests were averaged and the average displacement observed at 1 million cycles was 0.74mm.
Rotational Stability
Distal locking does more than simply provide axial strength for weight bearing. In unstable fractures, distal locking provides rotational stability as well. To determine the rotational stability afforded by the distal Talons™, a complete Talon™ DistalFix™ Proximal Femoral Nail was implanted in a composite femur and a rotationally unstable subtrochanteric fracture was created. A dial was fixed to the distal fragment (just below the fracture) and a pin was placed in the proximal fragment (just above the fracture). The specimen was tested with a cyclic load (98N to 980N) applied to the femoral head at 2Hz for 100,000 cycles. The pin position with respect to the dial was recorded at regular intervals and the results are reported in the graph. The cumulative rotation through the fracture site was 2°. This rotation occurred within the first 10,000 cycles, suggesting that early on the nail settled in and then remained fixed henceforth.